What Must Be True for a Baby to Suffer From Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn?
What is Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN)?
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) is also known by other names, including alloimmunization, isoimmunization, claret incompatibility, or blood sensitization. It can range from very balmy, with minimal to no fetal furnishings, to very severe requiring fetal therapy. Anybody has unique proteins (antigens) on the surface of their carmine blood cells. When our bodies are exposed to cherry-red blood cells that do non friction match our own, the immune arrangement produces additional proteins (antibodies) that volition mark those foreign red claret cells for destruction. At that place are two ways to be exposed to blood that does not lucifer our own: pregnancy or a blood transfusion. In one case antibodies have been made, they are present for the rest of our life.
If a woman has made antibodies, either as a outcome of a prior pregnancy or blood transfusion, and she becomes pregnant, those antibodies can cross the placenta. If the fetus carries red blood cell proteins that are not compatible with maternal blood, the maternal antibodies may crusade destruction of the fetal ruby blood cells. If enough fetal red blood cells are destroyed, fetal anemia will occur. Since HDN usually occurs during pregnancy, and less commonly through a blood transfusion, this rarely causes fetal anemia in a showtime pregnancy. However, once it appears, it tends to become more than astringent with each subsequent affected pregnancy.
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) Diagram
The most mutual red claret cell incompatibility is due to the Rh protein (also chosen D protein). Rh disease is the only incompatibility that can be prevented through administration of a special treatment chosen "immune globulin" during times of potential exposure to forestall antibody germination. It is recommended that all Rh-negative women receive Rho(D) allowed globulin during pregnancy and afterward commitment if there is a possibility that the begetter of the baby carries the Rh protein (is Rh positive). Other proteins that can cause HDN include Kell, Duffy, and Kidd, along with many others. These less common causes cannot exist prevented with allowed globulin.
How do I know if I have HDN?
Information technology is routine to obtain a blood test called Type and Screen on every pregnant adult female at the beginning of her pregnancy. This identifies your claret type and checks for the presence of maternal antibodies that could cross the placenta and bear upon the fetus. If antibodies are nowadays (a "positive" antibody screen), further studies are needed to cheque the amount and type of antibodies present. The level of the antibodies is chosen a titer. When the titer reaches a level that could cause fetal anemia, it is called a disquisitional titer. With the exception of Kell antibodies, we would non expect fetal anemia to occur without a critical titer.
What will happen during pregnancy?
When a significant patient has a positive antibody screen, information technology is important to make up one's mind if the fetal claret blazon is incompatible with maternal blood blazon. In some cases, testing the father'south claret volition answer this question. For some of the incompatibilities, fetal blood type tin exist determined by cartoon maternal blood. Other times, an amniocentesis (removal of amniotic fluid from the uterus through a needle procedure) may be required to make up one's mind if fetal claret is compatible with maternal blood. In one case we decide if in that location is an incompatibility between the mother's blood type and the fetus's blood blazon (or if we are not sure), we follow the titers by testing maternal blood regularly throughout the pregnancy. If a critical titer is reached or if the antibody is to Kell antigens, the pregnancy is followed with weekly ultrasounds. Although some pregnancies volition need weekly ultrasounds early on in pregnancy, in most pregnancies this starts in the late second or early on third trimesters.
At the fourth dimension of ultrasounds, the blood flow to the fetal brain is measured through the peak systolic velocity (PSV) of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). Fetuses with anemia increase the flow of blood to the fetal brain. A specific ultrasound measurement of this blood period correlates with the likelihood of fetal anemia and tin can determine the need for a fetal blood transfusion. When fetal anemia is very astringent, information technology can lead to a condition called hydrops when swelling or excessive fluid can accumulate in the body. This fluid can be seen in the chest, belly, or pare. If untreated, hydrops can atomic number 82 to stillbirth. The goal of intensive blood and ultrasound screening is to enable intervention for anemia before progression to hydrops.
What happens if there is fetal anemia?
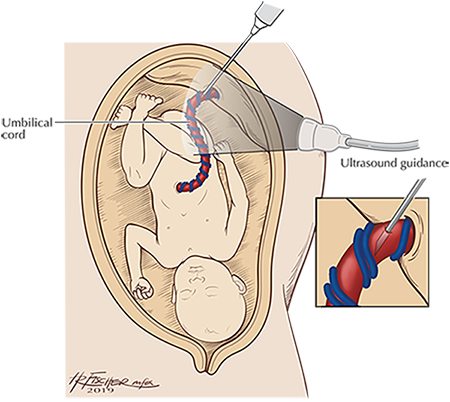
If fetal anemia is suspected, we recommend sampling the baby's blood through a procedure called cordocentesis. The cordocentesis is done under ultrasound guidance. A needle is placed into the fetal umbilical cord to sample the fetal claret, measure out the blood count, and perform a blood transfusion if needed. Many fetuses will need more one transfusion earlier the pregnancy is delivered.
Cordocentesis and Intrauterine Fetal Transfusion Diagram
What to expect at birth?
Fetuses that crave transfusions inside the uterus usually deliver betwixt 34 and 37 weeks' gestational historic period. About one-half of these newborns will require a transfusion afterward birth, and nigh all will require handling for jaundice (when skin, and possibly the white of eyes, turn a yellow colour due to buildup of bilirubin), ordinarily with phototherapy (exposure to fluorescent light bulbs or other sources of calorie-free). The newborn volition often need to be in the hospital longer than the mother. Some babies may be 4-6 months old before they completely recover the ability to make their own cherry-red claret cells, then they must exist closely followed by an experienced pediatrician.
Make an appointment
For more data or to schedule an appointment, phone call 734-763-4264.
Source: https://www.mottchildren.org/conditions-treatments/peds-fetal-medicine/hemolytic-disease-of-the-newborn-or-alloimmunization
0 Response to "What Must Be True for a Baby to Suffer From Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn?"
Post a Comment